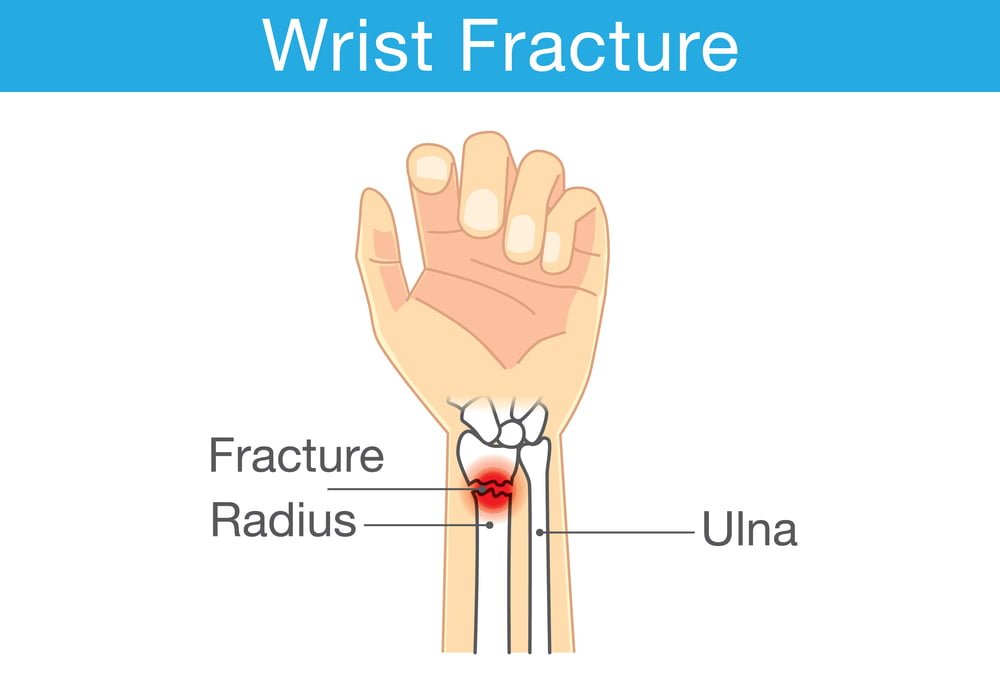
The forearm has two bones, and the radius is one of them. It is situated on the thumb side of the forearm, and the part that connects to the wrist joint is known as the distal radius. If this bone breaks near the wrist, it is referred to as a distal radius fracture. Typically, the fracture occurs when a person falls on their outstretched or flexed hand. It can also happen during a car accident, a cycling accident, a skiing accident, or any other sports activity.
A distal radius fracture may be isolated, which means that no other fractures are present. Alternatively, it can occur along with a fracture of the distal ulna, which is the forearm bone located on the small finger side. In such cases, the injury is referred to as a distal radius and ulna fracture.
Types of distal radius fracture
When the distal radius breaks, the type of fracture depends on the angle at which it breaks. There are two types: Colles and Smith fractures.
A Colles fracture occurs when the palm experiences direct impact, like when someone tries to break their fall with their hands and lands on their palms. The side view of the wrist after a Colles fracture can be likened to a fork facing downward, with a noticeable “bump” in the wrist resembling the neck of the fork. This happens because the broken end of the distal radius shifts upward towards the back of the hand.
On the other hand, a Smith fracture is less common and usually results from an impact to the back of the wrist, such as falling on a bent wrist. In this type of fracture, the end of the distal radius shifts downward towards the palm side, causing a noticeable drop in the wrist where the longer part of the radius ends.
Orthopedic implant for distal radius fracture
A distal radius plate is a surgical implant used to stabilize fractures of the distal radius, the end of the forearm bone that articulates with the wrist. Fractures of the distal radius are common, accounting for up to 20% of all fractures in adults. They are most commonly caused by a fall on an outstretched hand.
Distal radius fractures are one of the most common types of bone injuries, often caused by falls onto an outstretched hand. Treatment options for distal radius fractures include immobilization with a cast, closed reduction, or open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) with a distal radius plate. In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at the use of distal radius plates for treating these types of fractures.
Types of distal radius plates
Volar plates
These are also known as anterior plates or palmar plates, and are placed on the volar (palm) side of the radius bone. They are often used to treat distal radius fractures with dorsal displacement, which means the fractured bone has shifted towards the back of the wrist. Volar plates are designed to provide stability and support to the fracture site, allowing for proper healing.
Dorsal plates
These are also known as posterior plates, and are placed on the dorsal (back) side of the radius bone. They are often used to treat fractures that occur in the middle of the radius bone, and can be used in cases where the fracture has not displaced significantly. Dorsal plates are designed to provide stability and prevent the fracture from shifting during the healing process.
Locking plates
These plates have screws that lock into the plate, creating a more stable construct and reducing the risk of implant failure. Locking plates are often used in cases where there is poor bone quality or a high risk of the fracture site collapsing during the healing process.
Features of dorsal and volar plates
Distal radius plates can be implanted into the bone or placed on the outside of the bone, using screws to secure them in place. The location of the plate depends on the location and severity of the fracture. Major features include:
- Minimal irritation of ligaments and soft tissue: The plates have a flat profile, rounded edges, and polished surfaces, which reduces irritation of the ligaments and soft tissue.
- Some plates are precontoured: Some plates are precontoured to match the natural curvature of the bone, which reduces the need to bend them.
- A wide selection of plates for the best solution: There is a wide selection of plates available in different lengths and shapes, so the surgeon can choose the best plate for the specific fracture pattern.
- The plates do not have to be cut to size: The plates are available in different lengths and shapes, so they do not have to be cut to size, which saves time and reduces the risk of damaging the plate.
- Compatible with the LCP Compact Hand: The plates are compatible with the LCP Compact Hand system, which provides a comprehensive solution for hand surgery.
Materials of distal radius plates
Distal radius plates are made from a variety of materials, including metals and polymers. The most commonly used metals for these plates are titanium and stainless steel, both of which are biocompatible and can withstand the forces exerted on them during healing.
Titanium is particularly popular due to its high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and ability to integrate with bone tissue. Stainless steel, on the other hand, is more affordable and has a proven track record of success.
Polymers, such as polyether ether ketone (PEEK), are also sometimes used in the manufacture of distal radius plates due to their biocompatibility, low density, and ability to be molded into complex shapes. However, metal remains the most common choice for distal radius plates due to its strength and durability.
Benefits of distal radius plates
Distal radius plates offer a number of benefits, including:
- Stability: Distal radius plates provide stability to the fracture, which can help to prevent further injury and improve the healing process.
- Early mobilization: Distal radius plates allow for early mobilization of the wrist joint, which can help to prevent stiffness and improve overall recovery.
- Preservation of blood supply: Preservation of the blood supply to soft tissues and bone by gentle reduction techniques and careful handling.
- Reduced risk of complications: Distal radius plates can help to reduce the risk of complications, such as malunion and nonunion.
Risks of distal radius plates
Distal radius plates also have some risks, including:
- Infection: Infection is a rare but serious risk associated with any surgery.
- Nerve injury: Distal radius plates can increase the risk of nerve injury, especially if they are placed on the volar surface of the bone.
- Hardware failure: The screws or other hardware used to secure the plate to the bone can fail, which can require additional surgery to remove the plate.
Conclusion
The choice of implant for a patient depends on their unique injury, age, activity level, and overall health. Zealmax Ortho’s orthopedic implants are carefully crafted to be biocompatible, ensuring that the materials used are safe for the body and do not cause any negative reactions. These implants are also designed to be robust and resilient, supporting the healing process and facilitating the recovery of distal radius fracture.

